The world of trading is a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape where traders seek to gain an edge in the market by utilizing various strategies and tools. One such tool that has garnered significant attention in recent years is the Exponential Moving Average (EMA). EMAs are an indispensable part of a trader’s arsenal, aiding in the identification of trends and potential trading opportunities. In this comprehensive essay, we will delve into the art of trading with EMAs, exploring their various applications, strategies, and best practices.
(1) Understanding Exponential Moving Averages
Before we dive into how to trade using EMAs, it is crucial to understand the concept of Exponential Moving Averages. EMAs are a type of moving average that places more weight on recent price data compared to Simple Moving Averages (SMAs). This means that EMAs are more responsive to price changes, making them particularly effective for traders looking to capture short to medium-term trends.
EMAs are calculated using the following formula:
EMA = (Closing Price – EMA(previous day)) x Multiplier + EMA(previous day)
Where:
- Closing Price is the most recent closing price.
- EMA(previous day) is the EMA value of the previous day.
- Multiplier is calculated using the formula (2 / (n + 1)), where ‘n’ is the chosen period.
(2) Selecting the Right Trading Instrument
The first step in trading with EMAs is to select the trading instrument that aligns with your objectives. Whether you are interested in trading stocks, currencies, commodities, or cryptocurrencies, it’s essential to choose an asset class that you are familiar with and can analyze effectively. Each market has its unique characteristics, and understanding these nuances is pivotal to successful trading.
(3) Choosing the Appropriate Timeframe
Selecting the right timeframe or chart interval is a decision that can significantly impact your trading strategy. The choice of timeframe should align with your trading style and objectives. Common timeframes include 1-minute, 5-minute, 15-minute, 1-hour, daily, and weekly charts. For instance, day traders often prefer shorter timeframes, such as 1-minute or 5-minute charts, while swing traders might opt for daily or weekly charts to capture more extended trends. Your chosen timeframe should provide you with a clear picture of the market dynamics and match your trading horizon.
(4) Determining the EMA Periods
One of the key decisions when using EMAs is selecting the appropriate EMA periods. The EMA period represents the number of data points included in the calculation, and different EMA periods can serve different trading purposes. Common EMA periods include 9, 12, 26, 50, and 200. Shorter EMAs (e.g., 9 or 12) are highly responsive to short-term price movements, making them suitable for scalpers and day traders. Longer EMAs (e.g., 50 or 200) are better suited for identifying long-term trends and are favored by position traders.
(5) Plotting the EMAs on Your Chart
Once you’ve decided on the EMA periods that suit your trading style and goals, it’s time to plot these EMAs on your price chart. Most trading platforms offer EMA indicators that allow you to input the desired periods. For example, if you choose a 21-period EMA and a 50-period EMA, both lines will be displayed on your chart. These lines will move dynamically with price changes, helping you visualize the trend’s strength and direction.
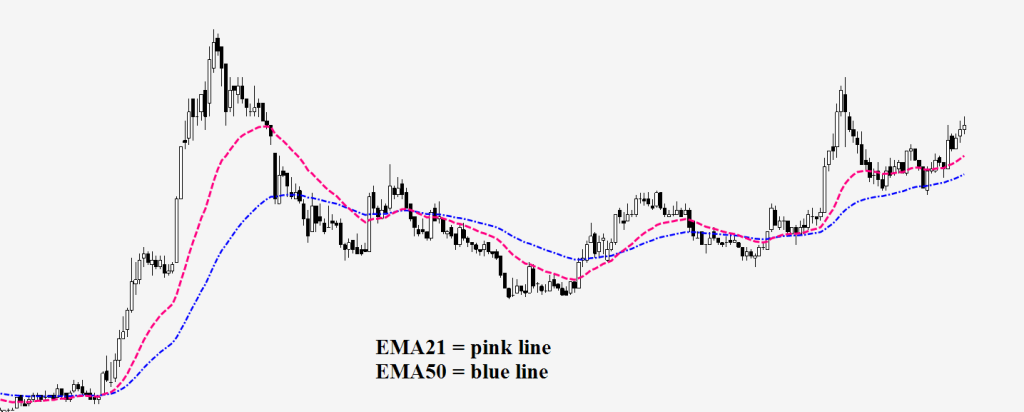
(6) Identifying EMA Crossovers
One of the most popular EMA trading strategies involves identifying EMA crossovers. A crossover occurs when two EMAs cross each other on the chart. There are two primary types of crossovers:
- Bullish Crossover: This occurs when the shorter EMA crosses above the longer EMA. It is considered a bullish signal, indicating a potential uptrend. Traders often look for confirmation of this signal before entering a long trade.
- Bearish Crossover: A bearish crossover happens when the shorter EMA crosses below the longer EMA. This is a bearish signal, suggesting a potential downtrend. As with bullish crossovers, traders typically seek confirmation before entering a short trade.
EMAs can serve as early warning signs of trend reversals or extensions, providing traders with valuable insights into market sentiment.

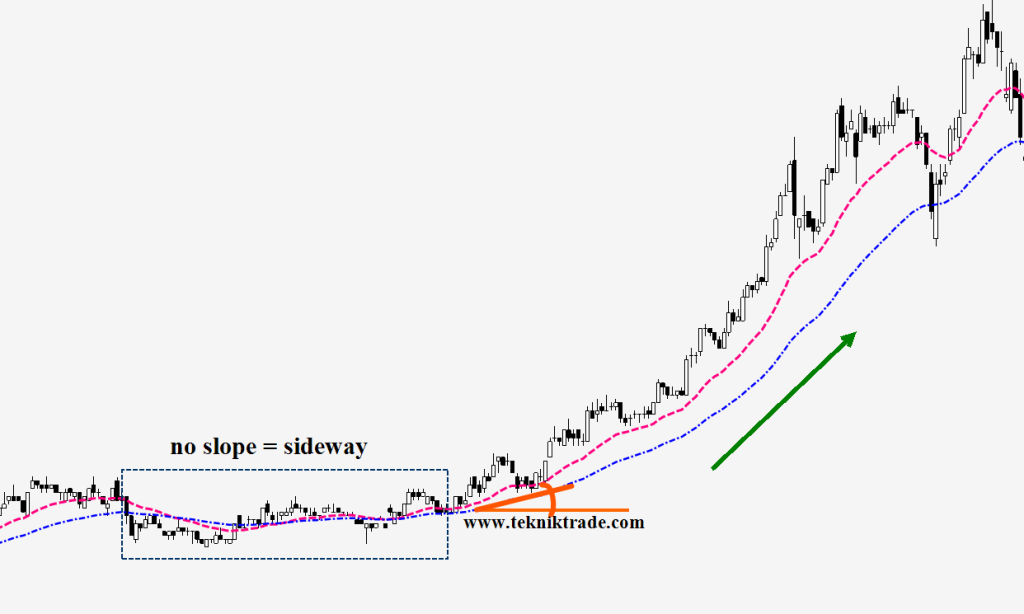
(7) Using EMA Slope
While EMA crossovers are a cornerstone of EMA-based trading, it’s also crucial to consider the slope or angle of the EMAs. The slope of an EMA line can provide valuable information about the strength of a trend. A steeply rising EMA indicates a strong bullish trend, while a steeply declining EMA suggests a robust bearish trend. Conversely, a flat EMA line signifies consolidation or a weaker trend. Traders can use this information to assess the vigor of the market and make more informed decisions.
(8) Setting Entry and Exit Points
Once you’ve identified EMA crossovers and assessed the slope, it’s time to set entry and exit points for your trades. These decisions should be based on a combination of factors, including EMA signals, the broader market context, and risk management principles.
For example, if you observe a bullish crossover where the shorter EMA crosses above the longer EMA, it may signal a potential uptrend. However, it’s essential to wait for additional confirmation, such as strong volume or other technical indicators, to reduce the risk of false signals. Likewise, setting a stop-loss order to limit potential losses and a take-profit order to secure profits is a fundamental aspect of any trading strategy.
(9) Combining EMAs with Other Indicators
While Exponential Moving Average, EMAs can be a powerful tool on their own, many traders combine them with other technical indicators to confirm trading signals and reduce false alarms. Some commonly used indicators include the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Stochastic Oscillator, and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). Integrating these indicators can provide a more comprehensive view of the market and improve the accuracy of your trading decisions.
(10) Risk Management
Successful trading is not only about identifying profitable opportunities but also about managing risk effectively. Risk management is crucial to safeguard your capital and minimize potential losses. When trading with Exponential Moving Average, EMAs or any other strategy, consider using the following risk management techniques:
- Set stop-loss orders: Determine a predetermined point at which you will exit a trade to limit losses if the market moves against you.
- Establish take-profit levels: Set profit targets to lock in gains when the market moves in your favor.
- Determine position size: Calculate the appropriate position size based on your risk tolerance and account size. Never risk more than you can afford to lose on a single trade.
- Diversify your trades: Avoid putting all your capital into a single trade or asset. Diversifying your portfolio can help mitigate risk.
- Maintain a risk-reward ratio: Ensure that your potential reward justifies the risk you are taking on a trade. A common guideline is to aim for a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2.
(11) Backtesting and Practice
Before implementing your EMA-based trading strategy with real money, it is advisable to backtest your approach on historical data. Backtesting involves applying your strategy to past market data to assess its performance and profitability. This process can help you refine your strategy and identify its strengths and weaknesses.
Additionally, practicing with a demo trading account can provide valuable experience without risking real capital. Demo accounts allow you to simulate real trading conditions and test your strategy in a risk-free environment. This practice can help you gain confidence in your trading decisions and fine-tune your approach.
Conclusion
Trading with Exponential Moving Averages is a dynamic and versatile strategy that can be adapted to various trading styles and objectives. By understanding the intricacies of exponential moving average, EMAs, selecting the right trading instrument and timeframe, and applying proper risk management techniques, traders can harness the power of EMAs to identify trends and make informed trading decisions.
While EMAs offer valuable insights into the market, it’s essential to remember that trading involves inherent risks, and there are no guarantees of success. A comprehensive approach to trading, which includes fundamental analysis, market awareness, and discipline, is critical for achieving consistent profitability. As you embark on your trading journey, keep in mind that continuous learning and adaptation are keys to long-term success in the financial markets.
DISCLAIMER for all posting and sharing on this website : https://www.tekniktrade.com/penafian-disclaimer/





















